Synthesis of paramagnetic dendritic silica nanomaterials with fibrous pore structure (Fe3O4@KCC-1) and their application in immobilization of lipase from Candida rugosa with enhanced catalytic activity and stability
Abstract
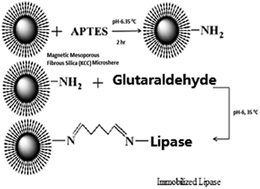
Paramagnetic mesoporous fibrous silica (Fe3O4@KCC-1) was prepared and its surface was functionalized with 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES) to obtain amino functionalized magnetic nanoparticles. Lipase from Candida rugosa was immobilized on functionalized magnetite Fe3O4@KCC-1-NH2 using glutaraldehyde (GLU) as the linker. The nanoparticles were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), vibrating sample magnetometry (VSM) and Fourier transformed infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). The characterization results revealed successful immobilization of lipase on functionalized magnetite with a saturation magnetization of 62.73 and 42.65 emu g−1 for magnetic nanoparticles and carbonyl functionalized carriers, respectively. The applied approach for support preparation, activation, and optimization of immobilization conditions, with a good lipase loading of 283 mg g−1 of carrier, provided better resistance to temperature and pH inactivation than free lipase and hence expanded the reaction pH and temperature regions, with an optimum pH of 6 and temperature of 35 °C. Immobilized Lipase Candida rugosa (ICRL) showed enzyme activity of 630 U g−1, maintained above 560.7 U g−1 (89%) of the initial activity after 28 days and 434.7 U g−1 (69%) after 10 cycles. Thus, ICRL showed improved storage stability and reusability.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...