Site-dependent electrochemical performance of Na and K co-doped LiFePO4/C cathode material for lithium-ion batteries
Abstract
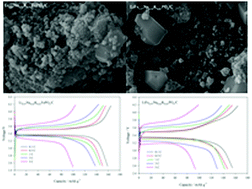
Olivine-type lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) has attracted much attention as a promising cathode material for lithium-ion batteries (LIBs). Na+ and K+ co-doped LiFePO4/C composite materials in two discrete sites, namely the Li1−x−yNaxKyFePO4/C or Li-site and LiFe1−x−yNaxKyPO4/C or Fe-site (x = 0.02, y = 0.01) were synthesized via solid-state reaction route, which is a simple and convenient method, particularly for mass production. The effects of Na and K occupied sites are studied by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Rietveld analysis, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) mapping, and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Furthermore, the electrochemical properties are evaluated by cyclic voltammograms (CVs), constant current charge/discharge cycling tests and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). It was observed that the co-doped samples exhibited improved electrochemical performances compared with the pristine LiFePO4/C material. The experimental results revealed that the Li0.97Na0.02K0.01FePO4/C composite had a higher capacity delivery and kinetics than LiFe0.97Na0.02K0.01PO4/C sample. It delivered a discharge capacity of 159 (0.1C), 150 (0.5C), 146 (1C), 138 (3C) and 100 mA h g−1 (5C).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...