Effects of isosteric substitutions on the conformational preference and cis–trans isomerization of proline-containing peptides†
Abstract
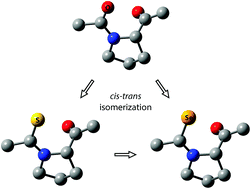
The effects of isosteric substitutions of the peptide C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O group by C
O group by C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) S and C
S and C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) Se on the conformational preference and prolyl cis–trans isomerization of Ac-Pro-NHMe and Ac-Ala-Pro-NHMe in water were studied using DFT methods. The isosteric replacement of a peptide bond resulted in changes in the preferences of the backbone conformation and puckering of the proline residue within both peptides depending on the substituent and its position (i.e., at the N- or C-termini). The polyproline II conformers with up puckering were highly populated in water for both Ac-ψ[CX-NH]Pro-NHMe and Ac-Ala-ψ[CX-NH]Pro-NHMe (X = O, S, and Se), although these peptides exist as ensembles of various conformers. For both peptides, the C
Se on the conformational preference and prolyl cis–trans isomerization of Ac-Pro-NHMe and Ac-Ala-Pro-NHMe in water were studied using DFT methods. The isosteric replacement of a peptide bond resulted in changes in the preferences of the backbone conformation and puckering of the proline residue within both peptides depending on the substituent and its position (i.e., at the N- or C-termini). The polyproline II conformers with up puckering were highly populated in water for both Ac-ψ[CX-NH]Pro-NHMe and Ac-Ala-ψ[CX-NH]Pro-NHMe (X = O, S, and Se), although these peptides exist as ensembles of various conformers. For both peptides, the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) X and C–N bond lengths became longer and shorter, respectively, in the order X = O, S, and Se, which is consistent with the values of the X-ray structures of the peptides. The isosteric substitutions at the N-terminus reduced the prolyl cis population in the order O < S < Se for Ac-Pro-NHMe, whereas there was a decrease and an increase in the cis population for Ac-Ala-Pro-NHMe with C
X and C–N bond lengths became longer and shorter, respectively, in the order X = O, S, and Se, which is consistent with the values of the X-ray structures of the peptides. The isosteric substitutions at the N-terminus reduced the prolyl cis population in the order O < S < Se for Ac-Pro-NHMe, whereas there was a decrease and an increase in the cis population for Ac-Ala-Pro-NHMe with C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) S and C
S and C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) Se, respectively. The rotational barriers to the prolyl cis–trans isomerization of Ac-Pro-NHMe and Ac-Ala-Pro-NHMe increased with the isosteric replacement in the order O < S < Se. The calculated changes in the cis population and rotational barriers are reasonably consistent with the observed results of the relevant peptides. The strength of the nN → π*C
Se, respectively. The rotational barriers to the prolyl cis–trans isomerization of Ac-Pro-NHMe and Ac-Ala-Pro-NHMe increased with the isosteric replacement in the order O < S < Se. The calculated changes in the cis population and rotational barriers are reasonably consistent with the observed results of the relevant peptides. The strength of the nN → π*C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) X interaction for the preferred trans conformer relative to the transition state and the difference in the overlap of the C–N bond for the two conformers are consistent with prolyl rotational barriers in the order O < S < Se. The results for isosterically substituted Ac-Pro-NHMe and Ac-Ala-Pro-NHMe reported here are expected to be useful for understanding the conformational preferences and cis–trans isomerization of other proline-containing peptides with C
X interaction for the preferred trans conformer relative to the transition state and the difference in the overlap of the C–N bond for the two conformers are consistent with prolyl rotational barriers in the order O < S < Se. The results for isosterically substituted Ac-Pro-NHMe and Ac-Ala-Pro-NHMe reported here are expected to be useful for understanding the conformational preferences and cis–trans isomerization of other proline-containing peptides with C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) S and C
S and C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) Se groups in the peptide backbone.
Se groups in the peptide backbone.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...