Poly(glutamic acid) hydrogels crosslinked via native chemical ligation†
Abstract
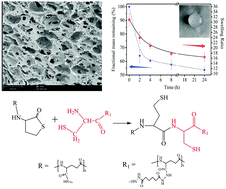
Mild crosslinking methods, which have a strong influence on biomedical hydrogels and scaffolds, have attracted wide attention in recent years. In this project, native chemical ligation (NCL) was utilized to prepare biocompatible and biodegradable hydrogels using naturally derived poly(glutamic acid) (PGA) with no additives or by-products. Firstly, thiolactone-grafted poly(glutamic acid) (PGA-HC) and cysteine-grafted poly(glutamic acid) (PGA-C) precursors were synthesized. Their structure was confirmed by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). Then, hydrogels crosslinked by NCL were formed by blending buffered solutions of PGA-HC and PGA-C with no additives under physiological conditions. After that, the equilibrium water content, morphology, degradation rate and mechanical properties of the hydrogels were characterized in detail. The data showed that the PGA hydrogels had gelation times, water contents and mechanical properties that were tunable by adjusting the precursor composition. Furthermore, the biocompatibility of the hydrogels was confirmed by an MTT assay. These characteristics provide a potential opportunity for the NCL hydrogels as wound dressings, skin fillings, drug delivery vehicles and tissue regeneration matrices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...