Calcination temperature as a probe to tune the non-enzymatic glucose sensing activity of Cu–Ni bimetallic nanocomposites†
Abstract
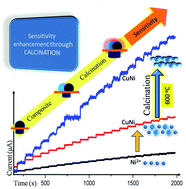
The present paper discusses the role of calcination in tuning the non-enzymatic glucose sensitivities of Cu–Ni bimetallic nanocomposites. Nanoparticles of Cu, a layered hydroxide of Ni and Cu–Ni nanocomposites were synthesized via the polyol reduction method. The prepared nanomaterials were thoroughly characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS). Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) was done in order to understand the thermal behavior of the nanoparticles. The prepared nanomaterials were subjected to calcination at three different temperatures viz. 400, 500 and 600 °C. The non-enzymatic glucose sensing activity of the nanomaterials was studied electrochemically. The nanocomposites showed the best sensing performance among the prepared nanomaterials. Interestingly, calcination resulted in a seven-fold increase in the sensitivity of the nanocomposites. The nanocomposite that was calcined at 600 °C showed the maximum sensitivity of 63.87 μA mM−1 cm−2 with a low detection limit of 8 μM at a signal to noise ratio of 3. The nanocomposite showed a distinct linear response in the range of 0.01 to 18 mM with a regression coefficient of 0.99162. The nanocomposite also exhibited excellent selectivity for glucose in the presence of other interfering agents. The nanocomposite also demonstrated good agreement with the pathology laboratory data for whole blood and blood serum samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...