Synthesis of different-sized SBA-15 nanoparticles and their fluoride release performances from poly(methyl methacrylate) dental restorative resin
Abstract
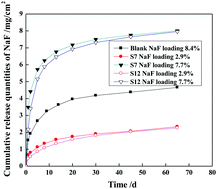
Mesoporous molecular sieve SBA-15 nanoparticles with different sizes were synthesized via a hydrothermal method using tetraethylorthosilicate as the silica source, tri-block copolymer Pluronic P123 as the structure-directing agent, and ethylene glycol and trisodium citrate as the organic modifiers in hydrochloric acid solution. In the absence of an organic modifier, high hydrochloric acid concentration favored the formation of SBA-15 nanorods with large diameters. The presence of ethylene glycol and trisodium citrate favored the formation of SBA-15 nanorods with small diameters at lower hydrochloric acid concentrations. Hydrochloric acid and the organic modifier synergistically affected the particle size, morphology, and dispersibility of the resultant SBA-15 nanoparticles. When the well-dispersed mesoporous SBA-15 nanoparticles were used as the NaF carrier in the poly(methyl methacrylate) resin matrix, the fluoride release rate was increased and the release time period was prolonged to at least 65 days. The reason may be that mesoporous SBA-15 nanoparticles constructed NaF diffusion channels and reservoirs, giving rise to a high fluoride release rate.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...