Highly stable water-soluble magnetic nanoparticles synthesized through combined co-precipitation, surface-modification, and decomposition of a hybrid hydrogel
Abstract
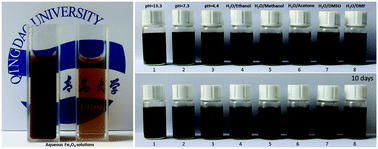
Water-soluble magnetic nanoparticles were synthesized using a method that combines co-precipitation, surface-modification, and decomposition of a hybrid hydrogel. The resulting Fe3O4 nanoparticles were analyzed by various analytical methods, including transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID), and dynamic light scattering (DLS). The results showed that the average size of the synthesized Fe3O4 nanoparticles was 7.7 nm and their surfaces were grafted with water-soluble polymer chains. The zeta potentials of aqueous Fe3O4 solutions were measured as −34.1 mV, −68.3 mV and −60.5 mV at pH 5.3, 7 and 11.3, respectively. Furthermore, the stability of the magnetic nanoparticles was found to be good not only in aqueous media of different pHs but also in mixed solvents of water and hydrophilic organic solvents, including ethanol, methanol, acetone, dimethyl sulphoxide (DMSO), and dimethylformamide (DMF).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...