High activity of aluminated bifunctional mesoporous silica nanoparticles for cumene hydrocracking and measurement of molar absorption coefficient†
Abstract
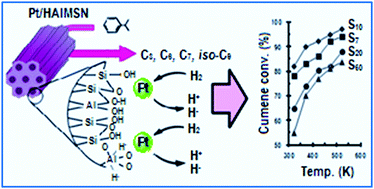
Bifunctional mesoporous silica nanomaterials (MSN) with various Si/Al molar ratios of 7, 10, 20 and 50 in platinum supported (Pt/HAlMSN) were synthesized using sol–gel methods followed by post-synthesis methods. XRD and nitrogen sorption results confirmed the mesoporous structure with surface areas of 537–775 m2 g−1. 27Al NMR spectroscopy confirmed aluminium loading with tetrahedral, pentahedral and octahedral structures. Pyridine adsorption IR results indicated that incorporation of aluminium led to the generation of strong Brønsted and Lewis acidic sites. Catalytic activity was investigated for cumene hydrocracking in a pulse microcatalytic reactor in the temperature range of 323–573 K which revealed that this activity depends on the number of Lewis and Brønsted sites. The high yield of cumene conversion increased from Si/Al molar ratios of 50 to 10 and decreased for the Si/Al molar ratio of 7 due to the presence of pentahedral Al and/or inactive tetrahedral Al atoms in Pt/HAlMSN-7. The high selectivity of α-methylstyrene showed the important role of Lewis acid sites in these bifunctional catalysts. In spite of the coke formation in the Pt/HAlMSN catalysts, reactivation recovered the activity of the catalysts after 100 h of reaction. The molar absorption coefficients of Pt/HAlMSN were measured using pyridine followed by water adsorption monitored by FTIR.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...