Preparation of copper nanoparticle-improved polyamide 6 composites by an in situ solution route with cupric oxide as the metallic copper source and investigation of their properties
Abstract
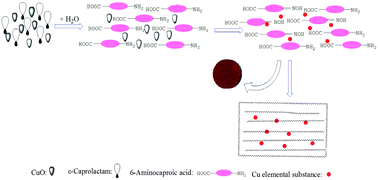
A novel in situ solution synthesis strategy is adopted to prepare polyamide 6 (denoted as PA6) filled with copper nanoparticles (denoted as nano-Cu), in which a CuO filler as the source of nano-Cu is directly reduced to metallic Cu by the amino group possessing weak reducing capability of PA6. As-prepared nano-Cu–PA6 composites are characterized by means of transmission electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction. Moreover, the ultraviolet-visible light absorption behavior, the thermal stability, and the friction and wear behavior of as-prepared nano-Cu–PA6 composites are also investigated in relation to the reinforcing effect of metallic Cu nanoparticles. Findings indicate that the CuO filler can be readily reduced to metallic Cu by the reducing atmosphere in which the filled PA6 composites are prepared. Besides, the dosage (mass fraction) of CuO has a significant effect on the crystalline form of PA6, and γ crystalline form of PA6 is predominant when a higher dosage of CuO is used to fabricate nano-Cu–PA6 composites. Moreover, introducing an appropriate amount of CuO fillers favors the generation of nano-Cu–PA6 composites with improved mechanical properties and wear resistance. Particularly, the nano-Cu–PA6 composite prepared at a CuO content of 0.5% possesses the best tensile strength and wear resistance, showing promising application as a functional polymer–matrix composite.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...