Influences of the molecular structure of carbon sources on the structure, morphology and performances of the Li3V2(PO4)3–C cathode for lithium ion batteries
Abstract
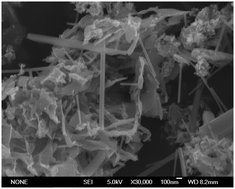
The influences of carbon sources in the synthesis of Li3V2(PO4)3–C (LVP) by carbothermal reduction method have been investigated. All the Li3V2(PO4)3–C samples possess the typical monoclinic structure. Of all the samples, LVP-PR (phenolic resin) possesses the largest discharge capacities of 128.4 mA h g−1, 125.7 mA h g−1 and 103.9 mA h g−1 at 0.2 C, 2 C and 5 C respectively. Its charge transfer resistance has the lowest value of 59.04 Ω. These excellent electrochemical performances result from its maximum conductivity of 1.93 × 10−2 S cm−1. The intensity ratio of peaks 1350 cm−1 to 1580 cm−1 in Raman spectra of LVP-PR has the lowest value of 1.162. The appearance of needle-shaped crystallites in LVP-PR and LVP-ER (epoxy resin) shows that phenolic resin and epoxy resin possess a strong reduction ability. This is also verified by the size of the crystallite. All these are because of the structural differences of carbon sources. The certain amount of benzene rings in the phenolic resin enables LVP-PR to possess high conductivity. The space steric effect of the methyl in epoxy resin and the lack of conjugated π bonds in glucose decrease the conductivity of LVP-ER and LVP-GL.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...