Enhancement of antimicrobial activity by co-administration of poly(propylene imine) dendrimers and nadifloxacin†
Abstract
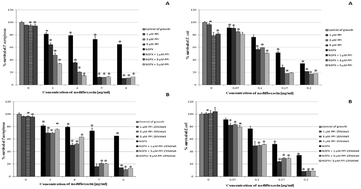
Despite the studies of dendrimers for biomedical application, the antibacterial activity of dendrimers has not been extensively explored. In the presented study we evaluate the antimicrobial activity of poly(propylene imine) dendrimers (PPI-G4) and their derivatives modified with maltose (PPI-25%mG4) in combination with nadifloxacin against Gram-negative bacteria Escherichia coli ATCC 25922, Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 15442 and Proteus hauseri ATCC 13315. Cytotoxicity of all studied dendrimers and nadifloxacin was investigated in a Chinese hamster fibroblast cell line (B14), a human liver hepatocellular carcinoma cell line (HepG2), a mouse neuroblastoma cell line (N2a) and a rat liver cell line (BRL-3A). The obtained results indicate that co-administration of nadifloxacin and studied dendrimers enhances the antimicrobial activity of the antibiotic against Gram-negative bacteria, at concentrations that are at the same time harmless to the eukaryotic cell lines. Moreover, the contribution of dendrimers allows using lower doses of the antibiotic.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...