A novel label-free fluorescence aptamer-based sensor method for cocaine detection based on isothermal circular strand-displacement amplification and graphene oxide absorption
Abstract
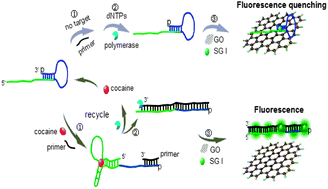
A label-free fluorescence aptamer-based sensor method for cocaine detection has been constructed based on polymerase aided isothermal circular strand-displacement amplification (ICSDA) and graphene oxide (GO) absorption. In this assay, a hairpin probe (HP), which consists of the aptamer sequence of cocaine, is partially complementary to the primer. When cocaine was bound with the HP, the primer could anneal with the single-stranded sequence of the opened HP and then trigger polymerase elongation, generating a double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) and displacing the cocaine. In the absence of cocaine, the HP remained intact and ICSDA would not occur. Through combining the unique properties of SYBR Green I (SG) and the preferential binding of GO to single-stranded DNA over dsDNA, a significant fluorescence enhancement was achieved. Whereas, the SG-stained HP without polymerase elongation was absorbed and quenched by GO. The proposed method is simple, convenient, and has high sensitivity and selectivity. This method displayed a good linear correlation within the cocaine concentration range from 0.2 μM to 100 μM, and the detection limit was down to 190 nM. In addition, this aptamer-based sensor method was also successfully applied for cocaine quantification in human urine samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...