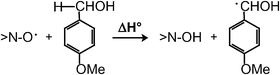
New mediators of laccase have been comparatively evaluated and ranked towards the benchmark aerobic oxidation of p-MeO-benzyl alcohol. The mechanism of oxidation of this non-phenolic substrate by each mediator, which is initially oxidised by laccase to the Medox form, has been assessed among three alternatives. The latter make the phenoloxidise laccase competent for the indirect oxidation of non-phenolic (and thus ‘unnatural’) substrates. Experimental characterisation of the mediators, by means of spectrophotometric, electrochemical and thermochemical survey, is reported. Clear-cut evidence for the formation of a benzyl radical intermediate in the oxidation of a particular benzyl alcohol with laccase and a ![[double bond splayed left]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e009.gif) N–OH mediator is attained by means of a trapping experiment. The selectivity of the laccase-catalysed oxidation of two competing lignin and polysaccharide model compounds has been assessed by using the highly proficient 4-MeO-HPI mediator, and found very high in favour of the former model. This evidence is in keeping with the operation of a radical hydrogen-abstraction process that efficiently cleaves the benzylic rather than the aliphatic C–H bond of the two models. Significant is the finding that catechol, i.e., a model of recurring phenolic structures in lignin, once oxidised to aryloxyl radical by laccase is capable to mediate a radical oxidation of non-phenolic compounds. This supports a fully-fledged role of laccase as a delignifying enzyme in nature by way of no other mediators than the very phenolic groups of lignin. Finally, an evaluation of the dissociation energy of the NO–H bond of HBT, which is not accessible experimentally, is provided by the use of a thermochemical cycle and theoretical calculations.
N–OH mediator is attained by means of a trapping experiment. The selectivity of the laccase-catalysed oxidation of two competing lignin and polysaccharide model compounds has been assessed by using the highly proficient 4-MeO-HPI mediator, and found very high in favour of the former model. This evidence is in keeping with the operation of a radical hydrogen-abstraction process that efficiently cleaves the benzylic rather than the aliphatic C–H bond of the two models. Significant is the finding that catechol, i.e., a model of recurring phenolic structures in lignin, once oxidised to aryloxyl radical by laccase is capable to mediate a radical oxidation of non-phenolic compounds. This supports a fully-fledged role of laccase as a delignifying enzyme in nature by way of no other mediators than the very phenolic groups of lignin. Finally, an evaluation of the dissociation energy of the NO–H bond of HBT, which is not accessible experimentally, is provided by the use of a thermochemical cycle and theoretical calculations.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
![[double bond splayed left]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e009.gif) N–OH mediator is attained by means of a trapping experiment. The selectivity of the laccase-catalysed oxidation of two competing
N–OH mediator is attained by means of a trapping experiment. The selectivity of the laccase-catalysed oxidation of two competing 

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...