Monoglyceride surfactants from arginine: synthesis and biological properties
Abstract
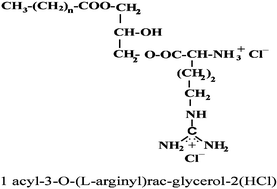
A novel family of dicationic arginine-monoglyceride surfactants, 1-acyl-3-O-(L-arginyl)-rac-glycerol·2HCl, was synthesised and characterised. They have one alkyl chain of with length in the range of C10–C14 attached to the glycerol though esters bonds and a dicationic polar head from the arginine. Structurally they can be regarded as analogues of the monoglycerides, widely used as emulsifiers in the food and in the pharmaceutical industry. The introduction of the basic amino acid arginine into the monoglycerides increases the solubility of these compounds and improves their antimicrobial activity. Moreover, the acute toxicity of these surfactants against Daphnia magna is clearly lower than the toxicity reported for conventional cationic surfactants.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...