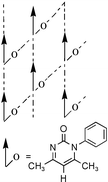
In a recent paper (New J. Chem., 2001, 25, 1520), we have analysed crystal structures of some N-aryl pyrimidinones. Based on the occurrence of two-dimensional layers in six out of nine crystals, we proposed that self-assembly in these structures might be analysed in terms of the stacking of 2D hydrogen-bonded layers. We show herein that meta-substituted phenyl pyrimidinones (Br, I, F, NO2, Me, OMe) have an overwhelming preference for the 2D polar arrangement, namely the parallel alignment of 1D chains within a layer. The molecules are arranged in chains mediated by C–H⋯O hydrogen bonds and such motifs are connected via C–H⋯O and C–H⋯halogen interactions in the lateral direction. A notable feature in these structures is that chains of dipolar molecules align in a parallel fashion to produce polar layers. The preference for 2D polarity is explained by the shape of the aryl pyrimidinone molecule and the geometry of interactions between hydrogen bonding functional groups (C–H donors, O/halogen acceptors). However, the polar layers stack in an anti-parallel manner and the crystal structures are centrosymmetric. The task of controlling parallel stacking of polar domains in the 3D crystal is a continuing challenge in our studies.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...