Silica-based multifunctional nanodelivery systems toward regenerative medicine
Abstract
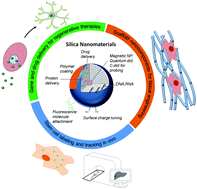
Silica-based nanomaterials (SiNMs) with different forms, including nanoparticles, nanorods and nanofibers either with a dense, porous or hollow structure, have been demonstrated as fascinating platforms for the delivery of therapeutic molecules in the inorganic nanocarrier regime. This is primarily due to their unique physicochemical properties, which are effective and tunable for the uptake of different cargo molecules, as well as to their biological responses favorable for cells and tissues. Over the last decade, a substantial number of studies have exploited SiNMs with different shapes, sizes, mesopore structures and surface charges for use in cancer therapy, imaging and bioseparation. In particular, their surface can be functionalized with candidate molecules from dyes to drugs for theranostic purposes. Moreover, providing the carriers with intelligent modes, such as stimuli-responsiveness, and with multifunctionality through combining them with imaging particles (magnetic nanoparticles, quantum dots and carbon dots) improves their therapeutic and diagnostic potential. While many pioneering works in the SiNM systems have focused on cancer therapy, there is growing demand for using SiNMs in the area of regenerative medicine, for stem cell therapy and tracking, and for the repair of dysfunctional tissues. Here we review the most recent advances in SiMNs that are available for regenerative therapies. For this, we first give an overview of the general nanostructure forms and characteristics of the SiNMs from a physicochemical and biological point of view, and then deal with the intracellular uptake mechanism and toxicity issues. Finally, advanced designs of SiNMs to provide multifunctional and intelligent actions of loading and delivery of drugs and molecules are detailed, and then perspectives for their potential uses in regenerative medicine are provided.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Recent Review Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...