5,6-Benzoflavones as cholesterol esterase inhibitors: synthesis, biological evaluation and docking studies†‡
Abstract
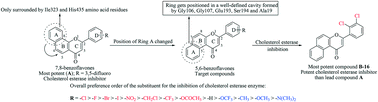
In a continued effort to develop potent cholesterol esterase (CEase) inhibitors, a series of 5,6-benzoflavone derivatives was rationally designed and synthesized by changing the position of the benzene ring attached to the flavone skeleton in previously reported 7,8-benzoflavones. All the synthesized compounds were checked for their inhibitory potential against cholesterol esterase (CEase) using a spectrophotometric assay. Among the series of forty compounds, seven derivatives (B-10 to B-16) exhibited above 90 percent inhibition against CEase in an in vitro enzymatic assay. Compound B-16 showed the most promising activity with an IC50 value of 0.73 nM against cholesterol esterase. To determine the type of inhibition, enzyme kinetic studies were carried out for B-16, which revealed its mixed-type inhibition approach. Moreover, to figure out the key binding interactions of B-16 with the amino acid residues of the enzyme's active site, molecular protein–ligand docking studies were also performed. B-16 completely blocks the catalytic assembly of CEase and prevents it from participating in the ester hydrolysis mechanism. The favorable binding conformation of B-16 suggests its prevailing role as a CEase inhibitor. Overall, the study showed that the cis-orientation of ring A with respect to the carbonyl group of ring C is responsible for the potent CEase inhibitory activity of the newly synthesized compounds.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...