Rational design and characterization of a DNA/HDAC dual-targeting inhibitor containing nitrogen mustard and 2-aminobenzamide moieties†
Abstract
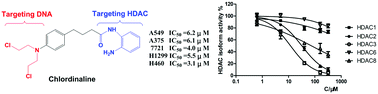
Histone deacetylases (HDACs) play a key role not only in gene expression but also in DNA repair. Herein, we report the rational design and characterization of a compound named chlordinaline containing nitrogen mustard and 2-aminobenzamide moieties as a DNA/HDAC dual-targeting inhibitor. Chlordinaline exhibited moderate total HDAC inhibitory activity. The HDAC isoform selectivity assay indicated that chlordinaline mostly inhibits HDAC3. Chlordinaline exhibited both DNA and HDAC inhibitory activities and showed potent antiproliferative activity against all the six test cancer cell lines with IC50 values of as low as 3.1–14.2 μM, which is significantly more potent than reference drugs chlorambucil and tacedinaline. Chlordinaline could induce the apoptosis and G2/M phase cell cycle arrest of A375 cancer cells. This study demonstrates that combining nitrogen mustard and 2-aminobenzamide moieties into one molecule is an effective method to obtain DNA/HDAC dual-targeting inhibitors as potent antitumor agents. Chlordinaline as the first example of such DNA/HDAC dual-targeting inhibitors could be a promising candidate for cancer therapy and could also be a lead compound for further optimization.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...