Synthesis of surface capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles for pH-stimuli responsive drug delivery applications
Abstract
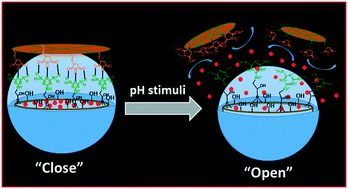
Mesoporous silica-based drug delivery carriers mostly require appropriate surface modifications to improve their drug delivery efficiency and to reduce their adverse side effects. In the present work, we have synthesised mesoporous silica nanoparticles and their surface was covered by using capping units such as tetrathio-maleimide (TTM) via a “host–guest” complexation mechanism for pH-responsive drug delivery applications. The surface-functionalised melamine (Mela) groups on the outer surface of the mesoporous silica nanoparticles act as “hosts” and the surface capped TTM units act as “guests” during the surface capping of the mesoporous silica nanoparticles via the “host–guest” complexation approach. After the encapsulation of cargoes into the mesopore channels, the melamine functional groups were covalently immobilised onto the outer surface of the cargo loaded MSNs and then the TTM units were introduced onto the outer surface of the silica nanoparticles as “gatekeepers” to obtain surface capped mesoporous silica (MSN@Mela@TTM/RhB) NPs to protect the loaded cargo molecules inside the mesopore channels and to prevent their premature leakage. The surface-capped TTM units controlled the drug release behavior with respect to the pH of the release medium. In this study, we used rhodamine B (RhB) as a model cargo to study the loading and pH-responsive release behavior of the MSN@Mela@TTM NPs. The encapsulated RhB molecules were retained inside the mesopore channels at physiological pH (pH 7.4) conditions while an enhanced release occurred at acidic pH (pH 5.0 and 4.0) conditions, respectively. Furthermore, the in vitro biocompatibility and the intracellular uptake efficiency of the synthesised MSNs@Mela@TTM NPs were examined by using the MDA-MB-231 cell line. The experimental results suggest that the MSNs@Mela@TTM nanoparticles are biocompatible and could be utilised for pH-stimuli responsive drug delivery applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...