Synthesis and antitumor mechanism of a new iron(iii) complex with 5,7-dichloro-2-methyl-8-quinolinol as ligands†‡
Abstract
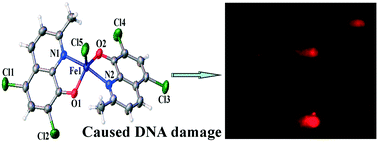
A new iron(III) complex with 5,7-dichloro-2-methyl-8-quinolinol (HClMQ) as ligands, i.e., [Fe(ClMQ)2Cl] (1), was synthesized and evaluated for its anticancer activity. Compared to the HClMQ ligand, complex 1 showed a higher cytotoxicity towards a series of tumor cell lines, including Hep-G2, BEL-7404, NCI-H460, A549, and T-24, with IC50 values in the range of 5.04–14.35 μM. Notably, the Hep-G2 cell line was the most sensitive to complex 1. Mechanistic studies indicated that complex 1 is a telomerase inhibitor targeting c-myc G-quadruplex DNA and can trigger cell apoptosis via inducing cell cycle arrest and DNA damage.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...