Novel soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors with a dihydropyrimidinone scaffold: design, synthesis and biological evaluation†
Abstract
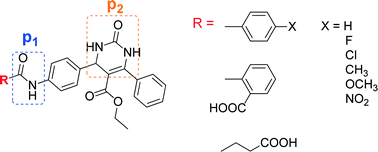
Inhibition of a soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) enzyme leads to high levels of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids which are involved in the regulation of blood pressure and vascular inflammation. The most potent sEH inhibitors reported in the literature are urea-based ones which often have poor bioavailability. In this study, a series of amide derivatives with a dihydropyrimidinone ring as a novel secondary pharmacophore against the sEH enzyme were designed, synthesized and biologically evaluated. Most of the synthesized compounds have considerable in vitro sEH inhibitory activity in comparison with 12-(3-adamantan-1-yl-ureido)-dodecanoic acid (AUDA), a potent urea-based sEH inhibitor. The docking results revealed that the designed compounds fit in the active site pocket properly and have suitable distances for effective hydrogen binding from three important amino acids, e.g. Tyr383, Tyr466 and Asp335. In agreement with the docking studies, most of the synthesized compounds have considerable in vitro sEH inhibitory activity in comparison with AUDA. Moreover, ADME properties of the compounds were analyzed in silico, and the results showed good predictions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...