Activation of a silent phenazine biosynthetic gene cluster reveals a novel natural product and a new resistance mechanism against phenazines†‡
Abstract
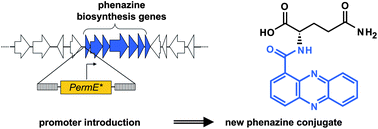
The activation of silent biosynthetic gene clusters is a principal challenge for genome mining strategies in drug discovery. In the present study, a phenazine biosynthetic gene cluster was discovered in the Gram-positive bacterium Streptomyces tendae Tü1028. This gene cluster remained silent under a multitude of cultivation conditions, both in the genuine producer strain and in a heterologous expression strain. However, introduction of a constitutive promoter upstream of the phenazine biosynthesis genes led to the production of phenazine-1-carboxylic acid (PCA) and of a new derivative thereof, i.e. a conjugate of PCA and L-glutamine. The linkage of PCA to L-glutamine by amide bond formation was catalyzed by enzymes of the heterologous expression host Streptomyces coelicolor M512. PCA showed a strong antibiotic effect, but PCA-Gln did not. Glutamination of PCA therefore appears to represent a resistance mechanism against the antibiotic PCA, which can be produced in significant quantities in soil by Pseudomonas strains. The gene cluster also contained genes for all enzymes of the mevalonate pathway and for an aromatic prenyltransferase, thereby resembling gene clusters for prenylated phenazines. However, purification and biochemical investigation of the prenyltransferase proved that it does not prenylate phenazines but hydroxynaphthalene substrates, showing very similar properties as NphB of naphterpin biosynthesis (Kuzuyma et al., Nature, 2005, 435, 983–987.).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...