Proteomic analysis reveals Xuesaitong injection attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by elevating pyruvate dehydrogenase-mediated aerobic metabolism
Abstract
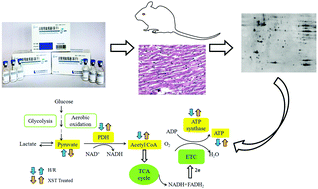
Xuesaitong injection (XST), which mainly consists of Panax notoginseng saponins, has been widely used for treating cardio-cerebral vascular diseases. However, the underlying mechanisms of XST associated with its cardioprotective effects are still unclear. To identify the potential target proteins of XST, two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2-DE)-based proteomics was utilized to analyze the protein profile of myocardium in rats with myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury. The differentially expressed proteins were identified by matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. It is interesting that XST can alter the expression of 7 proteins, including pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 alpha (PDHA1), hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase (HADHA), peroxiredoxin 3 (PRX3), gamma-enolase, acetyl-coenzyme A acyltransferase 2 (ACAA2), etc. Functional analysis revealed that those proteins were chiefly related to cardiac energy metabolism and oxidative stress. The cardioprotective effects of XST were further validated in H9c2 cardiac muscle cells with hypoxia/reoxygenation injury. We found that XST can promote the activity of PDH, an important enzyme related to the TCA cycle, as well as increase the intracellular content of acetyl-CoA and ATP. Moreover, XST also attenuated intracellular MDA release in H2O2-injured cardiac cells. This is the first study on the proteomic expression of XST-treated myocardium with I/R injury to reveal that the cardioprotective effects of XST may be attributed to the PDH-mediated restoration of aerobic glucose oxidation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...