Biochemical effects of venlafaxine on astrocytes as revealed by 1H NMR-based metabolic profiling
Abstract
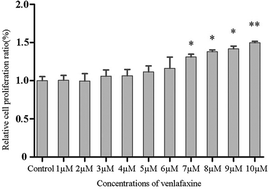
As a serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor [SNRI], venlafaxine is one of the most commonly prescribed clinical antidepressants, with a broad range of antidepressant effects. Accumulating evidence shows that venlafaxine may target astrocytes to exert its antidepressant activity, although the underlying pharmacological mechanisms remained largely unknown. Here, we used a 1H nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)-based metabonomics method coupled with multivariate statistical analysis to characterize the metabolic profiling of astrocytes treated with venlafaxine to explore the potential mechanism of its antidepressant effect. In total, 31 differential metabolites involved in energy, amino acid and lipid metabolism were identified. Ingenuity pathway analysis was used to identify the predicted pathways and biological functions with venlafaxine and fluoxetine. The most significantly altered network was “amino acid metabolism, cellular growth and proliferation”, with a score above 20. Certain metabolites (lysine, tyrosine, glutamate, methionine, ethanolamine, fructose-6-phosphate, and phosphorylethanolamine) are involved in and play a central role in this network. Collectively, the biological effects of venlafaxine on astrocytes provide us with the further understanding of the mechanisms by which venlafaxine treats major depressive disorder.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...