Applying random forest and subtractive fuzzy c-means clustering techniques for the development of a novel G protein-coupled receptor discrimination method using pseudo amino acid compositions
Abstract
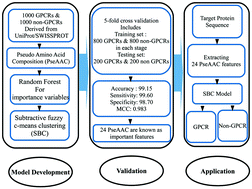
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) constitute the largest superfamily of integral membrane proteins (IMPs) and they tremendously contribute in the flow of information into cells. In this study, the random forest (RF) and the subtractive fuzzy c-means clustering (SBC) methods have been used to determine the importance of input variables and discriminate GPCRs from non-GPCRs using twenty amino acid and fifty pseudo amino acid compositions derived from GPCR sequences. The studied dataset was retrieved from the UniProt/SWISSPROT database and consists of 1000 GPCR and 1000 non-GPCR reviewed sequences. The top ranked RF-SBC-based model discriminates GPCRs and non-GPCRs successfully with the accuracy, sensitivity, specificity and Matthew's coefficient correlation (MCC) rates of 99.15%, 99.60%, 98.70% and 0.983%, respectively. These rates were obtained from averaged values of 5-fold cross validation using only twenty four out of fifty pseudo amino acid composition features. The results show that the proposed RF-SBC-based model outperforms other existing algorithms in terms of the evaluated performance criteria. The webserver for the proposed algorithm is available at http://brcinfo.shinyapps.io/GPCRIden.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...