Serum metabolomics analysis reveals impaired lipid metabolism in rats after oral exposure to benzo(a)pyrene†
Abstract
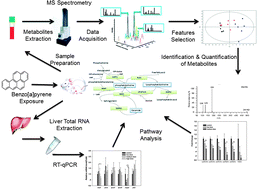
Benzo(a)pyrene [B(a)P] is ubiquitous in the environment. Although multiple toxicities have been reported for B(a)P, the impact of exposure to this chemical on metabolic networks remains obscure. In this study, a metabolomics approach based on ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry was used to investigate the disruption of global serum metabolic profiles in rats caused by exposure to B(a)P. Sprague–Dawley rats were treated with oral doses of 10, 100 and 1000 μg kg−1 B(a)P for 32 consecutive days. Distinct serum metabolomic profiles were associated with these doses. Twelve metabolites were identified as potential biomarkers and indicated that exposure to B(a)P disrupted both global amino acid metabolism and lipid metabolism, especially phospholipid and sphingolipid metabolism. Serum levels of lysophosphatidylcholines showed dose-dependent decreases, whereas serum levels of sphingomyelins showed dose-dependent increases. The expressions of some key genes involved in these pathways were also investigated. Expressions of enpp2, sms and smpd were significantly altered by exposure to high doses of B(a)P. Metabolic biomarkers were more sensitive than the corresponding gene expression for exposure to B(a)P. The findings of this study suggest potential novel mechanisms for the identified metabolic pathways.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...