Serum metabonomic analysis of apoE−/− mice reveals progression axes for atherosclerosis based on NMR spectroscopy†
Abstract
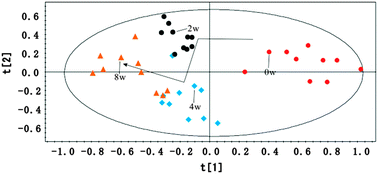
Atherosclerosis is a multifactorial and progressive disease commonly correlated with a high fat diet. The aim of this study was to identify potential biomarkers for the early diagnosis and monitoring of the progression of atherogenesis in apoE−/− mice using 1H NMR-based metabonomics. The apoE−/− mice were split into four groups according to the duration of high fat feeding (0 w, 2 w, 4 w and 8 w), and each group possessed different pathological characteristics. Serum 1H NMR-based metabonomics selectively captured the metabotypes that correlated with the degree of atherosclerosis, showing a time-dependent progression from the physiological to pathophysiological status. It was noted that changes in HDL, choline, taurine, glycine and glucose may be regarded as specific biomarkers of the early stage of atherosclerosis. With the progression of atherosclerosis, disorders in the metabolism of amino acids such as valine, alanine and methionine appeared when large atherosclerotic plaques existed. Multiple biochemical disorders involving lipid metabolism, energy and fatty acid metabolism were observed in the progression of atherosclerosis in apoE−/− mice. This study demonstrated that 1H NMR-based metabonomics can provide biochemical information about the progression of atherogenesis and offer a non-invasive means to discover potential biomarkers for the onset and development of atherosclerosis.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...