Computational delineation of tyrosyl-substrate recognition and catalytic landscapes by the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase domain†
Abstract
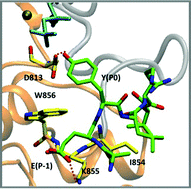
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK), which catalyzes protein phosphorylation reactions by transferring the γ-phosphoryl group from an ATP molecule to the hydroxyl group of tyrosine residues in protein substrates. EGFR is an important drug target in the treatment of cancers and a better understanding of the receptor function is critical to discern cancer mechanisms. We employ a suite of molecular simulation methods to explore the mechanism of substrate recognition and to delineate the catalytic landscape of the phosphoryl transfer reaction. Based on our results, we propose that a highly conserved region corresponding to Val852-Pro853-Ile854-Lys855-Trp856 in the EGFR tyrosine kinase domain (TKD) is essential for substrate binding. We also provide a possible explanation for the established experimental observation that protein tyrosine kinases (including EGFR) select substrates with a glutamic acid at the P − 1 position and a large hydrophobic amino acid at the P + 1 position. Furthermore, our mixed quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics (QM/MM) simulations show that the EGFR protein kinase favors the dissociative mechanism, although an alternative channel through the formation of an associative transition state is also possible. Our simulations establish some key molecular rules in the operation for substrate-recognition and for phosphoryl transfer in the EGFR TKD.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...