High-resolution magic angle spinning 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy detects choline as a biomarker in a swine obstructive chronic pancreatitis model at an early stage
Abstract
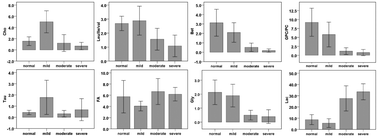
Chronic pancreatitis (CP) is a progressive inflammatory and fibrotic disease of the pancreas which encompasses a variety of clinical syndromes ranging from mild to life-threatening complications. Metabolomics has increasingly been applied to identify biomarkers for disease diagnosis with particular interest in diseases at an early stage. In this study, we tested a swine obstructive CP model by subtotal ligation of the main pancreatic duct, and the metabolic profiles of the Bama miniature swine pancreas were investigated using high-resolution magic angle spinning proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (HR MAS 1H MRS) combined with principal components analysis (PCA). Increases in lactate and choline for mild CP and decreases in glycerophosphocholine, phosphocholine, betaine and glycine were observed from normal pancreas to mild, moderate and severe CP. PCA results showed visual separations among the groups. The increase of choline at an early stage of CP and the decrease of glycerophosphocholine, phosphocholine, betaine and glycine reveal the pathogenesis of CP at a molecular level. The MRS results presented here demonstrate the potential of metabolic profiles in discriminating a normal pancreas from different stages of CP, which may be used to achieve CP early diagnosis and timely intervention to prevent irreversible destruction of the pancreas.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...