The effect of Rho-associated kinase inhibition on the proteome pattern of dissociated human embryonic stem cells†
Abstract
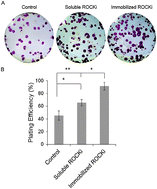
Rho-associated kinase (ROCK) is an immediate downstream target of the Rho GTPase signaling pathway which participates in transducing the Rho GTPase signal to the actin cytoskeleton, leading to the assembly of focal adhesions and stress fibers. Competitive inhibition of ROCK enhances post-thaw viability, improves cloning efficiency and decreases anoikis in human embryonic stem cells (hESCs). The molecular mechanisms by which ROCK inhibition mediates such responses are largely unknown. We have investigated the effect of Y-27632, a competitive ROCK inhibitor (ROCKi), on the proteome of hESCs. HESCs were exposed to ROCK inhibition directly by the addition of Y-27632 to the culture medium or to the Matrigel substratum. ROCK inhibition significantly increased cell survival and plating efficiency without any changes to the morphology, karyotype, or expression of pluripotency markers. We used a two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2-DE) coupled with tandem mass spectrometry based protein identification and identified 29 ROCKi responsive proteins. As expected, cytoskeleton-related proteins comprised the major ROCKi responsive proteins. Differential proteomic analysis showed that ROCKi induced upregulation of some actin binding proteins such as tropomyosin, F-actin capping protein (CapZ) and transgelin and downregulation of tubulin. In addition, ROCK inhibition was accompanied by changes in expressions of some chromatin modifying proteins such as SMARCB1, ILF3, and Dpy-30-protein, further suggesting a link between ROCK inhibition and the epigenetic mechanism of gene regulation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...