Switching p53 states by calcium: dynamics and interaction of stress systems
Abstract
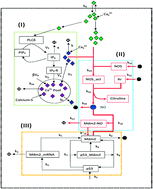
The integration of calcium and a p53–Mdm2 oscillator model is studied using a deterministic as well as a stochastic approach, to investigate the impact of a calcium wave on single cell dynamics and on the inter-oscillator interaction. The high dose of calcium in the system activates the nitric oxide synthase, synthesizing nitric oxide which then downregulates Mdm2 and influences drastically the p53–Mdm2 network regulation, lifting the system from a normal to a stressed state. The increase in calcium level switches the system to different states, as identified by the different behaviours of the p53 temporal dynamics, i.e. oscillation death to sustain the oscillation state via a mixed state of dampened and oscillation death states. Further increase of the calcium dose in the system switches the system from sustained to oscillation death state again, while an excess of calcium shifts the cell to an apoptotic state. Another important property of the calcium ion is its ability to behave as a synchronizing agent among the interacting systems. The time evolution of the p53 dynamics of the two diffusively coupled systems at stress condition via Ca2+ shows synchronization between the two systems. The noise contained in the system interestingly helps the system to maintain its stabilized state (normal condition). However, noise has the tendency to destruct the synchronization effect, which means that it tries to restrict the system from external signals to maintain its normal condition. However, at the stress condition, the synchronization rate is found to be faster.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...