A cellular lipidomic study on the Aβ-induced neurotoxicity and neuroprotective effects of EGCG by using UPLC/MS-based glycerolipids profiling and multivariate analysis†
Abstract
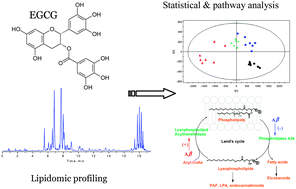
The aim of this study was to investigate the cellular lipid metabolism associated with β-amyloid peptide (Aβ)-induced neurotoxicity as well as the neuroprotective effect of (−)-epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), a major polyphenol in green tea. An ultra-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-Q-TOF-MS)-based lipidomic approach was developed to screen and identify changes of the glycerolipids (GL) upon Aβ treatment with or without the presence of EGCG in PC12 cells. Principle component analysis (PCA) showed that the Aβ-treated group was well separated from the control group, whereas the EGCG group was closer to the control group. The GL levels were significantly elevated in Aβ-treated cells compared with the control group, but were restored near to normal levels after EGCG treatment. The elevated phosphatidylcholines (PCs) levels observed in the Aβ-treated PC12 cells were quite probably the integrated results of the reduced phospholipase A2 (PLA2) activity and the enhanced activity of lysophospholipid acyltransferases. Moreover, an increased liberation of arachidonic acid (AA) from PCs was observed as another important response of PC12 cells to the Aβ aggregates, implying an active inflammatory process occurring in Aβ induced neurotoxicity. EGCG treatment can reverse the deregulated metabolism of PCs, which might be one of the biochemical mechanisms contributing to its neuroprotective effect. Collectively, results obtained from the current lipidomic analyses of PC12 cells provided important insight into the biochemical mechanisms underlying Aβ-induced neurotoxicity and neuro protective effects of EGCG. This is the first report of the lipidomic study on the neuroprotective effect of EGCG.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...