Global risk transformative prioritization for prostate cancer candidate genes in molecular networks†‡
Abstract
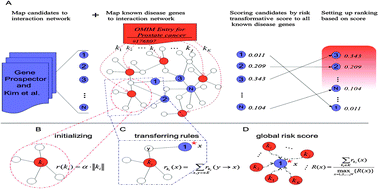
Understanding the pathogenesis of complex diseases is aided by precise identification of the genes responsible. Many computational methods have been developed to prioritize candidate disease genes, but coverage of functional annotations may be a limiting factor for most of these methods. Here, we introduce a global candidate gene prioritization approach that considers information about network properties in the human

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...