Controlled self-assembly of alginate microgels by rapidly binding molecule pairs†
Abstract
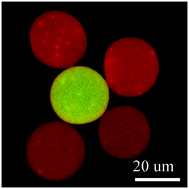
Controlled self-assembly of cell-encapsulating microscale polymeric hydrogels (microgels) could be advantageous in a variety of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine applications. Here, a method of assembly by chemical modification of alginate polymer with binding pair molecules (BPM) was explored. Alginate was modified with several types of BPM, specifically biotin and streptavidin and click chemistry compounds, and fabricated into 25–30 μm microgels using a microfluidic platform. These microgels were demonstrated to self-assemble under physiological conditions. By combining complementary microgels at a high ratio, size-defined assemblages were created, and the effects of BPM type and assembly method on the number of microgels per assemblage and packing density were determined. Furthermore, a magnetic process was developed to separate assemblages from single microgels, and allow formation of multilayer spheroids. Finally, cells were singly encapsulated into alginate microgels and assembled using BPM-modified alginate, suggesting potential applications in regenerative medicine.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...