Caulking polydimethylsiloxane molecular networks by thermal chemical vapor deposition of Parylene-C
Abstract
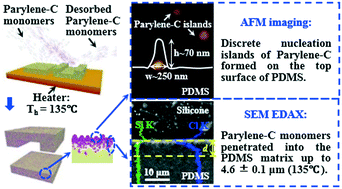
Surface functionalization of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) is important in developing high-performance microfluidic devices. This work applied the thermal chemical vapor deposition (t-CVD) of Parylene-C onto PDMS to caulk the molecular network while retaining the original surface properties for the oxygen plasma bonding. The very low deposition rates (for example, a nominal rate of 0.12 Å min−1 at 135 °C) of Parylene-C at elevated substrate temperatures enabled the reactive Parylene-C monomers to penetrate into the PDMS matrix up to 4.6 ± 0.1 μm (135 °C), which was verified for the first time by a scanning electron microscope with an energy dispersive X-ray analysis (SEM-EDAX). The Parylene-C caulked in the molecular network of PDMS matrix guaranteed an excellent resistance to small molecule permeations. Meanwhile, only discrete nucleation islands were formed on the top surface rather than a continuous Parylene-C layer as observed under the AFM scan, which made the processed PDMS surface ready for device assembly. This surface functionalization method has better long-term stability than the other wet-type rivals. The barrier for oxygen plasma bonding in previously reported dry surface treatments was also avoided, thereby, facilitating the device assembly. The present work successfully developed a novel pcPDMS (Parylene-C caulked PDMS) technique, which overcame the bonding difficulty in the previous works but retained the low small molecule permeability as before. Caulking a molecular network through the t-CVD of Parylene-C also demonstrated a new strategy of functionalizing polymer surfaces and preparing new hybrid materials for wide lab-on-a-chip applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...