High-throughput metabolic genotoxicity screening with a fluidic microwell chip and electrochemiluminescence†
Abstract
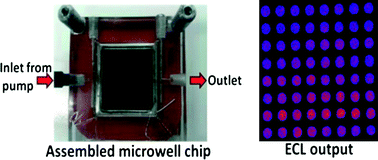
A high throughput electrochemiluminescent (ECL) chip was fabricated and integrated into a fluidic system for screening toxicity-related chemistry of drug and pollutant metabolites. The chip base is conductive pyrolytic graphite onto which are printed 64 microwells capable of holding one-μL droplets. Films combining DNA, metabolic enzymes and an ECL-generating ruthenium metallopolymer (RuIIPVP) are fabricated in these microwells. The system runs metabolic enzyme reactions, and subsequently detects DNA damage caused by reactive metabolites. The performance of the chip was tested by measuring DNA damage caused by metabolites of the well-known procarcinogen benzo[a]pyrene (B[a]P). Liver microsomes and cytochrome P450 (cyt P450) enzymes were used with and without epoxide hydrolase (EH), a conjugative enzyme required for multi-enzyme bioactivation of B[a]P. DNA adduct formation was confirmed by determining specific DNA-metabolite adducts using similar films of DNA/enzyme on magnetic bead biocolloid reactors, hydrolyzing the DNA, and analyzing by capillary liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (CapLC-MS/MS). The fluidic chip was also used to measure IC50-values of inhibitors of cyt P450s. All results show good correlation with reported enzyme activity and inhibition assays.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...