An investigation into dispersion upon switching between solvents within a microfluidic system using a chemically resistant integrated optical refractive index sensor†
Abstract
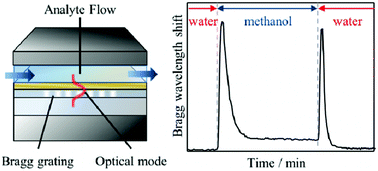
A planar Bragg grating device has been developed that is capable of detecting changes in the refractive index of a wide range of fluids including

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...