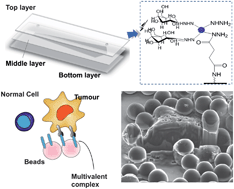
An in situ method of modifying the chemistry and topology of microfluidic surfaces in order to mimic the cellular environment is described. The binding of functionalised microbeads to microfluidic channels allows the surface-to-volume ratio of the system, and thus the number of biomolecules available for reaction, to be vastly increased, thereby enhancing the sensitivity of biochemical analyses. The sensitivity and specificity of the technique were first investigated via the study of carbohydrate–protein interactions. Beads featuring hydrazide moieties were adhered to the channel surface, after which carbohydrates (galactose and mannose) were bound to the beads in situ and reacted with fluorescently labelled proteins. Results showed a six-fold increase in fluorescent signal compared to the same process performed on a glass surface without the presence of beads, thereby demonstrating the increase in valence afforded by the method. In a subsequent study, beads, modified with galactose moieties via the in situ functionalisation technique, were used to perform studies of colon tumour cells from a cell sample. Here, the carcinoma cells exhibited superior adhesion than the normal cells due to an increased expression of active galactose receptors, thereby demonstrating the success of the biofunctionalisation method for investigating cellular mechanisms.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...