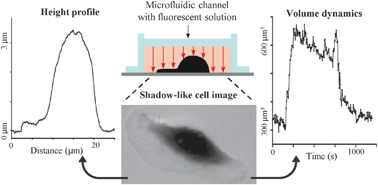
We propose a new technique to measure the volume of adherent migrating cells. The method is based on a negative staining where a fluorescent, non-cell-permeant dye is added to the extracellular medium. The specimen is observed with a conventional fluorescence microscope in a chamber of uniform height. Given that the fluorescence signal depends on the thickness of the emitting layer, the objects excluding the fluorescent dye (i.e., cells) appear dark, and the decrease of the fluorescent signal with respect to the background is expected to give information about the height and the volume of the object. Using a glass microfabricated pattern with steps of defined heights, we show that the drop in fluorescence intensity is indeed proportional to the height of the step and obtain calibration curves relating fluorescence intensity to height. The technique, termed the fluorescence displacement method, is further validated by comparing our measurements with the ones obtained by atomic force microscopy (AFM). We apply our method to measure the real-time volume dynamics of migrating fish epidermal keratocytes subjected to osmotic stress. The fluorescence displacement technique allows fast and precise monitoring of cell height and volume, thus providing a valuable tool for characterizing the three-dimensional behaviour of migrating cells.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...