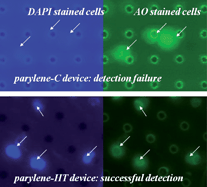
Parylene-C has been widely used as a biocompatible material for microfluidics and micro total analysis system (μTAS) applications in recent decades. However, its autofluorescence can be a major obstacle for parylene-C based devices used in applications requiring sensitive fluorescence detection. In this paper, Parylene-C was compared with other commonly used polymer and plastic materials in μTAS devices for their autofluorescence. We also report here an in-depth study of the behaviors and mechanisms of the autofluorescence of parylene-C, as well as several other commercialized members in the parylene family, including parylene-D, parylene-N and parylene-HT, using epifluorescence microscopy, fluorimeter and infrared spectroscopy. Strong autofluorescence was induced in parylene-C during short-wavelength excitation (i.e. UV excitation). Variation of autofluorescence intensity of parylene-C film was found to be related to both dehydrogenation and photo-oxidation. Moreover, the influence of microfabrication process on parylene-C autofluorescence was also evaluated. Parylene-HT, which exhibits low initial autofluorescence, decreasing autofluorescence behavior under UV excitation and higher UV stability, can be a promising alternative for μTAS applications with fluorescence detection.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...