Multiphase electropatterning of cells and biomaterials†
Abstract
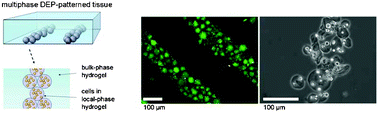
Tissues formed by cells encapsulated in hydrogels have uses in biotechnology, cell-based assays, and tissue engineering. We have previously presented a 3D micropatterning technique that rapidly localizes live cells within hydrogels using dielectrophoretic (DEP) forces, and have demonstrated the ability to modulate tissue function through the control of microscale cell architecture. A limitation of this method is the requirement that a single biomaterial must simultaneously harbor biological properties that support cell survival and function and material properties that permit efficient dielectrophoretic patterning. Here, we resolve this issue by forming multiphase tissues consisting of microscale tissue sub-units in a ‘local phase’ biomaterial, which, in turn, are organized by DEP forces in a separate, mechanically supportive ‘bulk phase’ material. We first define the effects of medium conductivity on the speed and quality of DEP cell patterning. As a case study, we then produce multiphase tissues with microscale architecture that combine high local hydrogel conductivity for enhanced survival of sensitive liver progenitor cells with low bulk conductivity required for efficient DEP micropatterning. This approach enables an expanded range of studies examining the influence of 3D cellular architecture on diverse cell types, and in the future may improve the biological function of inhomogeneous tissues assembled from a variety of modular tissue sub-units.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...