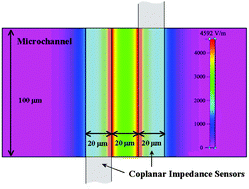
Glass-based microchannel chips were fabricated using photolithographic technology, and Pt thin-film microelectrodes, as coplanar impedance sensors, were integrated on them. Longitudinal design parameters, such as interelectrode spacing and electrode width, of coplanar impedance sensors were changed to determine AC frequency characteristics as design parameters. Through developing total impedance equations and modeling equivalent circuits, the dominant components in each frequency region were illustrated for coplanar impedance sensors and the measured results were compared with fitted values. As the ionic concentration increased, the value of the frequency-independent region decreased and cut-off frequencies increased. As the interelectrode spacing increased, cut-off frequencies decreased and total impedance increased. However, the width of each frequency-independent region was similar. As the electrode area increased, flow decreased but fhigh was fixed. We think that the decrease in RSol dominated over the influence of other components, which resulted in heightening flow and fhigh. The interelectrode spacing is a more significant parameter than the electrode area in the frequency characteristics of coplanar sensors. The deviation of experimentally obtained results from theoretically predicted values may result from the fringing effect of coplanar electrode structure and parasitic capacitance due to dielectric substrates. We suggest the guidelines of dominant components for sensing as design parameters.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...