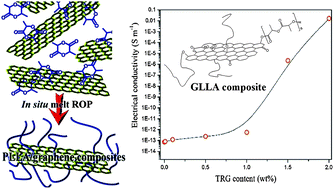
A series of poly(L-lactide) (PLLA)–thermally reduced graphene oxide (TRG) composites (GLLA) were prepared via the in situ ring-opening polymerization of lactide, with TRG as the initiator; after their preparation, the composites were characterized. By using a more effective method of synthesis, the thermal stability, crystallization rate, and electrical conductivity of PLLA were increased. The starting temperature for the thermal decomposition of PLLA was increased from 173 °C to 211 °C via the introduction of 2.00 wt% TRG sheets. At a TRG content of 2.00 wt%, the chemical interaction between the PLLA and the TRG sheets was strong enough to increase the nucleation rate and the overall crystallization rate of the PLLA. The electrical conductivity of the GLLA composites increased with increasing TRG content. Typical insulating–conductive percolation behavior was observed for TRG contents between 1.00 and 1.50 wt%, and the electrical conductivity of the PLLA was improved by 12 orders of magnitude in the GLLA composites, from 7.14 × 10−14 S m−1 for neat PLLA to 1.63 × 10−2 S m−1 for GLLA with 2.00 wt% of TRG sheets. These results demonstrate a straightforward means of preparing GLLA composites that perform satisfactorily in terms of their electrical conductivity and their thermal stability.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...