Antimicrobial efficacy and optimized cell adhesion from defined plasma polymerised multilayer structures involving zinc acetylacetonate and allylamine
Abstract
Plasma
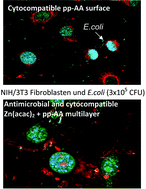
- This article is part of the themed collection: Materials for biosurfaces

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...