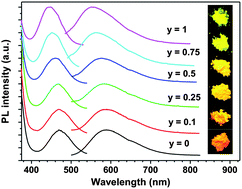
In this study, a new efficient Ce3+-doped fluorosulfide phosphor, Y2(Ca,Sr)F4S2:Ce3+, was obtained by using solid-state methods in a sealed silica ampoule. The synthesized Y2(Ca,Sr)F4S2:Ce3+ was characterized by powder X-ray diffraction and refined with Rietveld methods. Y2(Ca,Sr)F4S2:Ce3+ can be excited by blue light (440–470 nm) and shows yellow-to-orange broadband emission peaking at 553–590 nm with a quantum efficiency of 16–31%. Non-radiative transitions between Ce3+ ions in Y2CaF4S2:Ce3+ and Y2SrF4S2:Ce3+ hosts have also been demonstrated to be attributable to dipole–dipole interactions, and the critical distances were calculated to be 18.9 and 19.3 Å. The possible mechanism of the tunable luminescence properties was described on the basis of band structure calculations. In addition, a white LED device was fabricated by using Y2(Ca,Sr)F4S2:Ce3+ phosphor pumped with a 460 nm blue chip. The CRI value and CCT were measured to be 74–85 and 3500–8700 K, respectively, showing promising potential for solid-state lighting.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...