Chemical and biological decontamination functions of nanofibrous membranes
Abstract
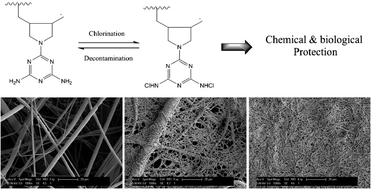
Novel composite membranes with poly(vinyl alcohol-co-ethylene-g-diallylmelamine) (PVA-co-PE-g-DAM) nanofibers layered on poly(propylene-g-diallylmelamine) (PP-g-DAM) meltblown nonwoven fabric were successfully developed as lightweight and breathable protective materials with chemical and biological decontamination functions. By controlling levels of coated nanofibers, three nanofibrous membranes with similar surface morphology, hydrophilicity and transport properties were prepared. The N-halamine precursor moieties in the membrane matrices can be converted to active N-halamine structures with a diluted sodium hypochlorite solution, and the active chlorine content on the membranes is rechargeable and durable. The chlorinated nanofibrous membranes demonstrated very powerful and rapid biocidal effects against both E. coli and S. aureus by contact, as well as excellent disinfection effect to wet bacterial penetration through the membrane. Furthermore, the efficient chemical detoxification functions of the halamine nanofibrous membranes were also observed by a total decontamination of

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...