A semiconductor–enzyme photoelectrode for oxygen reduction by direct transfer of photo-generated electrons to laccase
Abstract
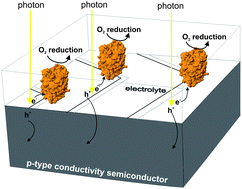
An electrochemically functionalized surface of p-type silicon was used as a nanostructured material for immobilization and activation of a redox metalloprotein. A protocol resulting in the stable enzyme adsorption and utilization was applied to Trametes versicolor laccase (TvL), the “blue” copper-containing oxidase enzyme, a model bio-electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction. The obtained system was tested as a photocatalytic electrode for oxygen sensing through its electroreduction at copper ionic active sites following illumination with visible light. Processes related to the photoexcitation and charge separation occur within the semiconductor (SC) material. Direct, rather than mediated by 2,2′-azinobis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonate) (ABTS), electron transfers from the semiconductor to the enzyme were observed. The topography of the p-Si substrate was assessed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and tapping mode atomic force microscopy (TM AFM) methods. The electronic properties of the systems were tested using synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy (SRPES). The nature of the biomolecule immobilization was studied by TM AFM.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...