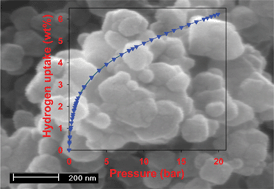
A commercially available zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF), namely Basolite Z1200 (BASF), has been used as template for nanocasting of highly microporous ZIF-templated carbon. The “hard template carbonization technique” consists of liquid impregnation of furfuryl alcohol into the pores of the ZIF followed by polymerization and then carbonization during which the ZIF template is removed to generate the microporous carbon (90–95% microporosity) with a surface area of 900–1100 m2 g−1 and a pore volume of ca. 0.7 cm3 g−1. Chemical activation (with KOH at a relatively low temperature of 700 °C for 1 h and a carbon/KOH weight ratio of 1 : 4) of the ZIF-templated carbons increases their porosity by between 30 and 240% depending on their carbonization temperature, to achieve a surface area of up to 3200 m2 g−1 and a pore volume of 1.94 cm3 g−1. Despite the drastic increase in porosity, the activated ZIF-templated carbons retain significant microporosity with micropores contributing 80–90% of surface area and 60–70% of pore volume. This occurs because the activation process mainly enhances existing porosity rather than creating new larger pores. The activation enhances the hydrogen uptake capacity of the ZIF-templated carbons by between 25 and 140% from 2.6–3.1 wt% to the range 3.9–6.2 wt% (at −196 °C and 20 bar). The increase in hydrogen uptake after activation is closely related to rises in the micropore surface area and micropore volume rather than overall increase in porosity. Due to their microporous nature, the carbons exhibit high hydrogen storage density in the range 13.0–15.5 μmol H2 m−2, which is much higher than that of most high surface area activated carbons.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...