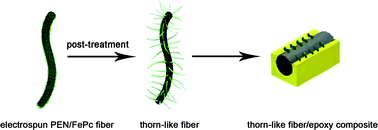
One of the most important aspects to take into account when dealing with composite materials is the filler–matrix interaction. This is particularly true in the case of nanofiber-reinforced composites. Here, we designed a new 3D architecture: growing thorns on an electrospun nanofiber surface, aiming to strengthen the fiber–matrix adhesion in engineered composite materials. The novel thorn-like fiber, composed of polyarylene ether nitriles (PEN) “stems” and iron phthalocyanine (FePc) “thorns”, was prepared by combining electrospinning and temperature-induced self-assembly. Especially, the FePc thorn-like structures could be grown on PEN nanofibers by a post-temperature treatment, and the lengths of the thorns could be finely controlled by the processing time and temperature, respectively. More importantly, after the thorn-like fibers were embedded into an epoxy resin, the thorns could tie molecules and interlock with the surrounding epoxy resin. The flexural properties of composites reinforced with these thorn-like fibers were further increased in comparison with that of neat and untreated fiber-reinforced epoxy resin, respectively. Thus, this functional fiber can be used as an effective composite reinforcement to polymer resins.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...