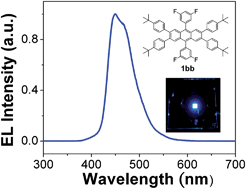
Fluorescent 2,3,6,7,9,10-hexaphenylanthracene-based derivatives (HPhAn) were synthesized to serve as deep-blue dopants in organic electroluminescent (EL) devices. The fluorescent emissions of HPhAn fluorophores, fine-tuned from 462 to 449 nm with varied fluorinated phenyl rings attached to the central carbons of the anthracene core, produced photoluminescence quantum yields of 82–88% in the solid state. Unlike the known monostyrylamine deep-blue dopant, these blue dopants in dilute solutions showed no pronounced spectral red shift with increasing solvent polarity; the emission color of HPhAn dopants is thus insensitive to the polarity of the medium. The highest-occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) and lowest-unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) energy levels calculated from the oxidation potentials and optical energy gaps are 5.61–5.70 eV and 2.73–2.89 eV, respectively. These thermally robust compounds undergo thermal decomposition at temperatures greater than 300 °C. The relationships among current density, voltage and luminance, the EL efficiency and the operational stability of devices based on the blue HPhAn dopants were examined. These HPhAn-doped EL devices are activated at voltages less than 3.5 V and attained an external quantum efficiency as much as 5.3% in the deep-blue light region with Commission Internationale d'Éclairage (CIE) coordinates (0.14, 0.10), near the National Television System Committee (NTSC) standard blue coordinates (0.14, 0.08).
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...